PCV Vaccine: Benefits and Risks
Protecting Health: Unveiling the Impact of PCV Vaccines

PCV Vaccine: Benefits and Risks
Pneumococcal disease, caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae, is a significant global health concern, particularly affecting young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems. The introduction of the Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) has been pivotal in reducing the incidence of pneumococcal infections and related complications worldwide. This blog post explores the PCV vaccine, its benefits, potential risks, and its impact on public health.
Understanding Pneumococcal Disease
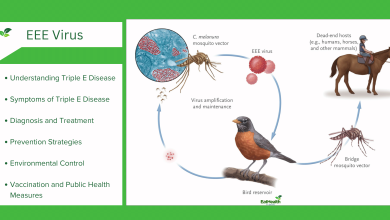
Pneumococcal disease encompasses a range of infections, including pneumonia, meningitis, bacteremia (blood infection), and otitis media (middle ear infection). The bacterium S. pneumoniae can spread through respiratory droplets and colonize the upper respiratory tract, leading to various infections that can be severe and life-threatening. Just as we know What are The Names of Childhood Vaccinations?
Types of Pneumococcal Infections
- Pneumonia: Infection of the lungs causing inflammation and difficulty in breathing.
- Meningitis: Infection of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, posing a risk of neurological damage.
- Bacteremia: Presence of bacteria in the bloodstream, which can lead to sepsis and organ failure.
- Otitis Media: Infection of the middle ear, particularly common in young children, causing pain and potential hearing loss.
Development and Types of PCV Vaccine
Development
The PCV vaccine was developed to prevent pneumococcal infections by inducing an immune response against the bacteria. The first PCV introduced was PCV7, which targeted seven strains of S. pneumoniae. Over time, newer versions like PCV10 and PCV13 have been developed to cover more strains, including those most commonly associated with severe disease.
Types
- PCV10: Protects against 10 strains of S. pneumoniae.
- PCV13: Protects against 13 strains, including those covered by PCV10 and additional serotypes known to cause disease.
Both vaccines are administered as a series of doses typically starting in infancy to provide early protection against pneumococcal infections.
Benefits of the PCV Vaccine
1. Prevention of Pneumococcal Infections
The primary benefit of the PCV vaccine is its ability to prevent pneumococcal diseases such as pneumonia, meningitis, and bacteremia. Vaccination reduces the likelihood of infection and related complications, particularly in vulnerable populations.
2. Reduction in Disease Burden
Since the introduction of PCV vaccines, there has been a significant decrease in pneumococcal disease incidence and related hospitalizations. This reduction has alleviated the burden on healthcare systems and improved overall public health.
3. Protection of High-Risk Groups
PCV vaccination is crucial for protecting high-risk groups, including young children, the elderly, and individuals with underlying medical conditions. Vaccination helps prevent severe illness and reduces transmission within communities.
4. Herd Immunity
High vaccination coverage leads to herd immunity, where the spread of S. pneumoniae is inhibited, protecting even those who are not vaccinated. This community-wide protection is essential for preventing outbreaks and reducing disease transmission.
5. Safe and Well-Tolerated
PCV vaccines have been extensively studied for safety and efficacy. They are generally well-tolerated, with common side effects being mild and temporary, such as redness or swelling at the injection site or mild fever.
Risks and Considerations
1. Potential Side Effects
While rare, PCV vaccines can cause mild side effects such as fever, irritability, or local reactions at the injection site. Serious allergic reactions are extremely rare but possible.
2. Vaccine Safety Monitoring
Ongoing surveillance and monitoring ensure the safety of PCV vaccines. Regulatory agencies and healthcare providers continuously assess adverse events to maintain public confidence in vaccination programs.
3. Limited Serotype Coverage
Despite protecting against multiple strains, PCV vaccines do not cover all serotypes of S. pneumoniae. Continued surveillance and development of new vaccines are necessary to address emerging strains and maintain effectiveness.
Global Impact and Implementation Challenges
1. Global Vaccination Initiatives
PCV vaccination is a critical component of national immunization programs worldwide. Initiatives like Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, have supported the introduction of PCV in low-income countries, expanding access and reducing disparities in vaccine coverage.
2. Challenges in Implementation
Challenges in implementing PCV vaccination programs include vaccine access, cold chain logistics, healthcare infrastructure, and vaccine hesitancy. Addressing these challenges is essential for achieving equitable vaccine coverage and maximizing health benefits.
Future Directions and Innovations
1. Next-Generation Vaccines
Research continues on developing new PCV formulations and technologies, including broader serotype coverage and alternative delivery methods, to enhance vaccine efficacy and accessibility.
2. Integrated Vaccination Strategies
Integrating PCV vaccination with other childhood vaccines and health interventions can optimize healthcare delivery and improve overall child health outcomes.
Conclusion
The PCV vaccine has revolutionized the prevention of pneumococcal diseases, significantly reducing morbidity and mortality globally. Its benefits in protecting vulnerable populations and reducing disease burden are well-documented, outweighing the potential risks associated with vaccination. Continued investment in vaccination programs, research, and global collaboration is essential to sustain these achievements and advance towards disease elimination.
By understanding the benefits and risks of the PCV vaccine, individuals and healthcare providers can make informed decisions and contribute to efforts aimed at preventing pneumococcal infections worldwide. From students learning about infectious diseases to experts shaping public health policies, the PCV vaccine remains a cornerstone in disease prevention and health promotion.