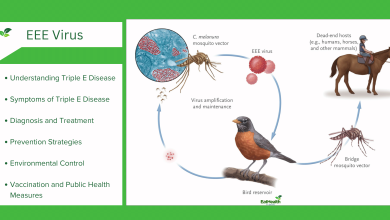
Medical Cure for the Treatment of Hepatitis A?
Navigating Hepatitis A Treatment: Medical Solutions and Innovations
Medical Treatment for Hepatitis A: A Comprehensive Overview
Hepatitis A, a viral liver infection, has been a persistent global health concern due to its ability to spread rapidly through contaminated food, water, and close contact. The good news is that medical science has made significant strides in developing effective for Hepatitis A Treatment.
Supportive Care and Rest
While Hepatitis A often resolves on its own without specific antiviral treatment, supportive care plays a critical role in managing the disease. Patients are typically advised to get plenty of rest, stay hydrated, and consume a well-balanced diet to aid the body’s healing process. Adequate rest allows the immune system to combat the virus effectively.
Hospitalization in Severe Cases
In severe cases of Hepatitis A, hospitalization might be necessary. This is particularly true when complications arise, such as acute liver failure. Hospital-based care ensures close monitoring of liver function, electrolyte levels, and overall health status. Intravenous fluids and other medications might be administered to address dehydration and maintain proper organ function.
Antiviral Medications
While Hepatitis A primarily resolves on its own, antiviral medications can help accelerate recovery and reduce the duration of symptoms. One such medication is ribavirin. However, its use is limited to severe cases and cases of immune-compromised individuals due to potential side effects.
Preventive Measures: Hepatitis A Vaccine
Prevention is a cornerstone of managing Hepatitis A. The most effective method of prevention is the Hepatitis A vaccine. This vaccine provides long-lasting immunity and is recommended for children, travelers to high-risk areas, individuals with chronic liver disease, and those who engage in high-risk behaviors. Timely vaccination not only prevents the disease but also contributes to community-wide protection.
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
In cases where an individual has been exposed to Hepatitis A, post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) might be recommended. This involves administering the Hepatitis A vaccine or immune globulin within a specified time frame to prevent the development of the disease. PEP is particularly important for individuals who are at high risk of complications.
Lifestyle Modifications
Patients diagnosed with Hepatitis A are often advised to abstain from alcohol and avoid certain medications that could further burden the liver. Engaging in alcohol or substances that stress the liver can impede the healing process and worsen the condition.
Conclusion
Medical advancements have significantly enhanced the treatment options available for Hepatitis A. While most cases resolve naturally, antiviral medications, supportive care, and hospitalization when needed play crucial roles in managing the disease. The primary emphasis, however, remains on prevention through vaccination, which has proven to be highly effective in curbing the spread of Hepatitis A. For those at risk of exposure, early intervention, adherence to medical advice, and responsible lifestyle choices are vital in ensuring a full recovery and reducing the potential impact of this viral infection on liver health.