Cautions After Attacking Diabetics
Navigating Post-Attack Considerations for Diabetic Patients: A Comprehensive Guide
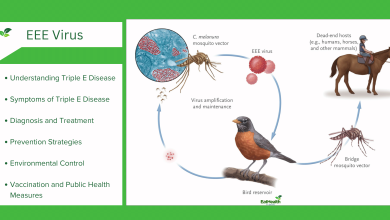
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions worldwide. Managing diabetes involves a delicate balance of lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring to maintain optimal blood glucose levels. Unfortunately, diabetic individuals are not immune to health challenges, and in some cases, they may experience acute medical emergencies such as heart attacks or strokes. The period following such an incident requires special caution and attention to ensure the best possible outcomes for these patients. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to the precautions and considerations that should be taken after an attack in individuals with diabetes.
1. Prioritize Medical Evaluation and Consultation
After experiencing a heart attack or stroke, individuals with diabetes must seek immediate medical attention. Diabetic patients are at a higher risk of cardiovascular complications due to the potential impact of diabetes on blood vessels and the heart. A thorough medical evaluation is essential to determine the extent of damage and identify any additional underlying conditions that may require treatment adjustments.
2. Glycemic Control
Maintaining stable blood glucose levels remains crucial even in the aftermath of a heart attack or stroke. Stress and illness can impact blood sugar levels, potentially leading to hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. Close monitoring of blood glucose levels and adjusting insulin or medication dosages as needed is essential to prevent further complications.
3. Medication Review and Adjustment
Post-attack, medications may need to be adjusted to ensure that they are effective and safe for individuals with diabetes. Certain medications, particularly those affecting the cardiovascular system, may interact with diabetes medications. A review of the medication regimen by a healthcare professional is vital to prevent adverse reactions and ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
4. Diet and Nutrition
A heart attack or stroke can have significant implications on dietary considerations for diabetic patients. A registered dietitian or nutritionist can help tailor a balanced meal plan that aligns with both cardiovascular health and diabetes management goals. This plan should consider the reduction of saturated and trans fats, sodium, and added sugars, while focusing on lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
5. Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is beneficial for both cardiovascular health and diabetes management. However, post-attack, individuals may need to adjust their exercise routines based on their medical condition and the recommendations of their healthcare provider. Gradual re-entry into physical activity is advised, along with close monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, and blood sugar levels during exercise.
6. Psychological Support
Recovering from a heart attack or stroke can take a toll on mental health. Diabetic patients may experience anxiety, depression, or heightened stress levels during this time. Psychological support, such as counseling or support groups, can provide an outlet for expressing feelings and learning coping strategies.
7. Preventive Measures
Post-attack, it’s essential to focus on preventive measures to reduce the risk of future cardiovascular events. Quitting smoking, managing cholesterol levels, controlling blood pressure, and adhering to prescribed medications are critical steps in preventing further complications.
The aftermath of a heart attack or stroke in diabetic patients requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to ensure optimal recovery and long-term health. From medical evaluation to medication adjustments, diet modifications, psychological support, and preventive measures, every aspect of care must be carefully considered. By following these precautions, individuals with diabetes can take control of their health, mitigate future risks, and work towards a better quality of life. Collaboration between the patient, healthcare providers, and support networks is paramount in this journey to recovery.